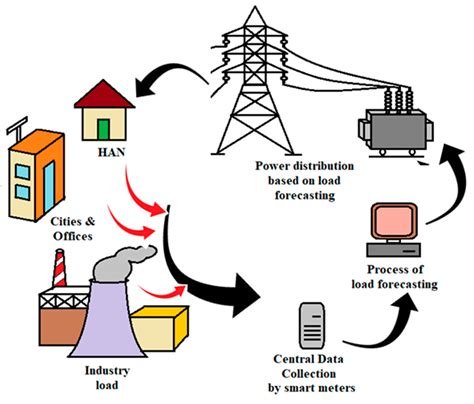
Understanding Ethereum’s BIP30: Utilizing Vulnerability
Ethereum’s transfer to the (POS) certificate (POS) to the consensus algorithm, and the introduction of a new network, BIP30 (Bitcoin suggestion 30), have raised concerns among cryptocurrency and safety experts. One of the most significant vulnerabilities revealed by this change is the potential utilization, known as “NetSplit” or “fork Netsplit”.
What is NetSplit?
The Netsplit refers to a scenario where the attacker is seeking a network, causing division in the history of the block chain. This can lead to the imbalance of the toe, which makes it difficult to use legal users for their assets. To understand why this vulnerability exists, let us dive into the background and discussion of the BIP30.
Background discussion: bip30 and fork
The BIP30 was introduced as part of Ethereum’s transition from POW to POS. The purpose of this change was to reduce the energy consumption needed to safeguard the network by implementing a new consensus algorithm that rewards the validators by the stakes based on their contribution rather than mining. However, some stakeholders have expressed concern about the safety effects of this change.
One such concern is the potential of the fork, where the attacker can deliberately create a new block that has a different title situation (ie NetSplit), which shares the history of the block chain. This can lead to a network fork version, causing difficulties for legal users who rely on the original chain.
Exploit: How Abuse NetsPlit
In order to utilize the Netsplits and forks, the attacker should create a new block with a different title situation (i.e. NetSplit), which is not recognized by the existing block chain. This could be achieved by various means including:
- Creating a harmful block : An attacker can create a new block with a title -Hash that does not accept the network effectively by creating a fork.
- Genesis block
Manipulation: An attacker can edit the Genesis block (Blockchain’s first block) to introduce NetSPLIT, which makes it difficult for legal users to use their funding.
The consequences and mitigation
The utilization of the Netsplits and forks has a significant effect on the Ethereum ecosystem. Legal users may have difficulty accessing their funds, leading to losses and possible damage to the network.
Several measures have been taken to alleviate this risk:
- New Title Sleeits : Moving to POS introduced new title parts designed to be safer and more durable for manipulation.
- Prevent forks : Multiple procedures, including the introduction of the “hard fork” mechanism, try to prevent forks by ensuring that only applicable blocks can be added to the block chain.
conclusion
The vulnerability revealed by the BIP30 is a serious concern for the Ethereum ecosystem. To understand how this utilization works and which measures have been taken to alleviate it, it is necessary to deepen the BIP30’s surrounding background discussion. By looking at the concept of NetSplit and Forks, you can better appreciate the measures to be taken to prevent such exploitation.
As the cryptocurrency scenery continues to develop, understanding these complexities is crucial for investors, developers and users.